Bluehost Emails Stop Working After Switching to Netlify
by Samuele Lilliu | 5 February 2023

- Producer: Samuele Lilliu
- Software: DNS
by Samuele Lilliu | 5 February 2023
A Name Server is a critical component of the Domain Name System (DNS), which is responsible for converting human-readable domain names into IP addresses that computers can understand and communicate with.
When a domain name is registered, its associated Name Server information is also recorded. This information tells other Name Servers on the Internet where to find the authoritative Name Server for that domain, which holds the actual mapping of domain names to IP addresses.
When a user types a domain name into a web browser, the browser first contacts a Name Server to resolve the domain name to an IP address. The Name Server then returns the IP address to the browser, which can then establish a connection with the server hosting the website.
In short, Name Servers serve as intermediaries between domain names and IP addresses, enabling users to access websites using memorable domain names instead of numeric IP addresses.
If your domain name is registered with BlueHost but you have decided to host your website on Netlify, you will need to change the following DNS records:
It’s important to note that the exact process for changing these records may vary based on the specific hosting provider you are using. Before making any changes, it’s always a good idea to backup your current DNS configuration, so that you can revert to it if needed.
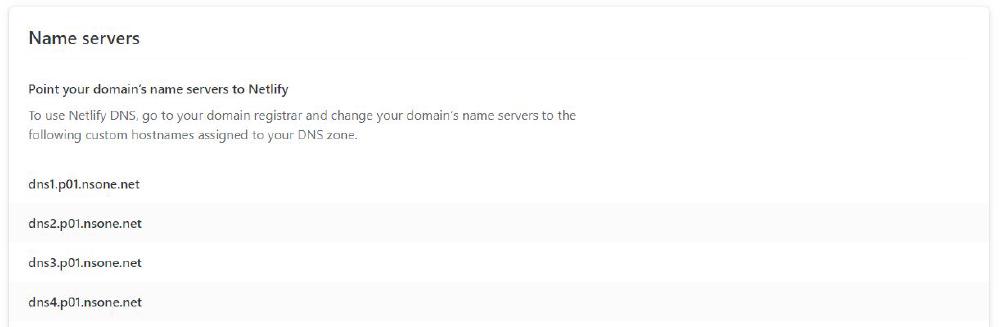
I initially just wrote down the Name Servers provided by Netlify under the Domains panel
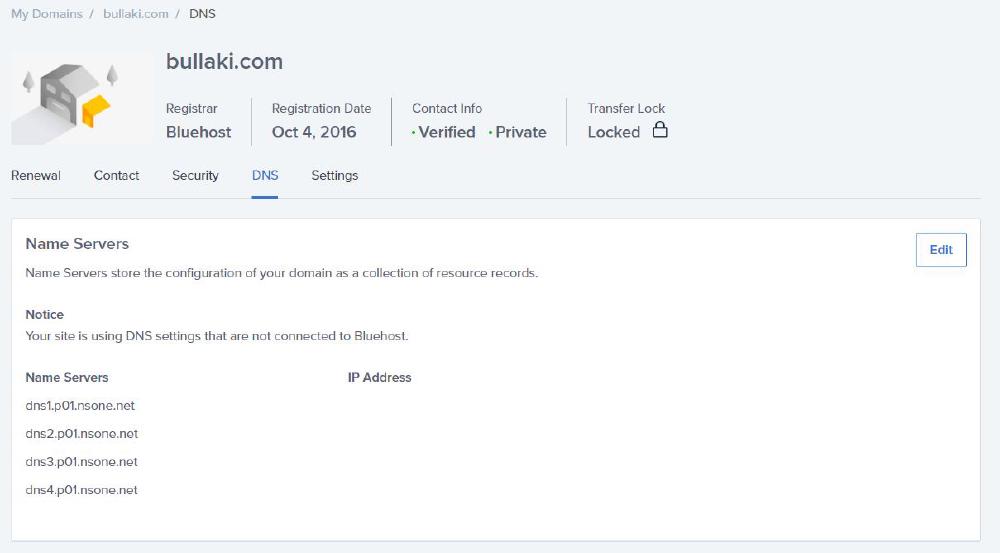
I entered them in the BlueHost DNS settings, where my domain is registered:
The time it takes for a Name Server change to propagate can vary, but it typically takes 24-48 hours for the changes to take effect globally. This time frame is known as DNS propagation.
During the propagation process, the updated Name Server information is distributed to other Name Servers on the Internet through a process called recursion. Essentially, the recursion process works by starting at the root Name Server and following the authoritative Name Server chain until it reaches the Name Server that holds the actual mapping of the domain name to its IP address.
Once the updated Name Server information has been obtained, the local Name Server caches the information for a specified time, known as the Time to Live (TTL). The TTL determines how long a Name Server should cache the information before it needs to be updated again.
It’s important to note that during the propagation process, some users may still be directed to the old IP address or site, while others may see the updated IP address and site. This is because different Name Servers around the world may have different cache expiration times for the same domain name.
The process actually took about 6 hours. But after that emails stopped working. Emails are currently being served by BlueHost. So what happened there? I got in touch with the BlueHost “custom service” but they were totally unhelpful. Some customers have reported that the quality of support they receive from BlueHost can be inconsistent, with some representatives being very helpful and others not being as knowledgeable. It’s a matter of luck. I wasn’t lucky.
A mail records, also known as MX records (Mail Exchange Records), are a type of DNS record used to manage email delivery for a domain. MX records specify the mail servers responsible for accepting email messages on behalf of a domain, and the priority of each mail server.
When an email is sent to a recipient at a domain, the sending mail server performs a DNS lookup to determine the MX records for the domain. The mail server then delivers the email to the mail server specified in the MX record with the highest priority.
Each MX record includes a priority value, which determines the order in which mail servers should be used if multiple mail servers are available. The mail server with the lowest priority value is used first, and if it’s unavailable, the email will be delivered to the next mail server with a higher priority value.
In summary, MX records are used to manage the delivery of email for a domain by specifying the mail servers responsible for accepting email messages, and the priority of each mail server.
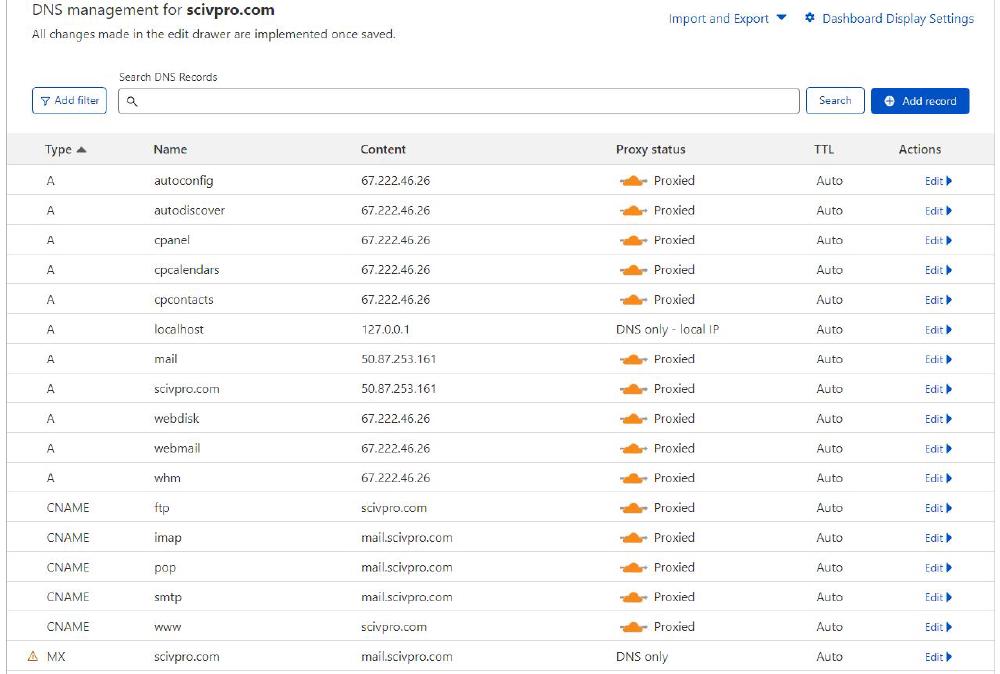
As I wrote above these records must be changed on Netlify to ensure emails managed by BlueHost work. I needed to add two extra records in the Netlify Domains panel, A and MX (first two lines).
The effect was immediate, there was basically no delay.
I found myself in a similar situation with another website. Both domain and website in this case are hosted by BlueHost. It’s a WordPress website, and due to slow performance, the server administrator suggested changing the Name Server to CloudFlare. Again, we did that email services, also provided by BlueHost, were interrupted. The solution was to change the IP address in the A mail and A scivpro.com records on the CloudFlare DNS panel to the right IP address (50.87.253.161). After that emails were back online.